- Docs
- /
Resumable Indexes
06 Jun 2022 18306 views 0 minutes to read Contributors ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Resumable Indexes in SQL Server
INTRODUCTION
On SQL Server 2007 CTP 2.0 there is an Alter Index feature to pause and resume indexes during maintenance, which offers several ways to maintain the indexes at a very granular level. Previous versions of SQL Server gave a different dimension to index maintenance operations, but this feature has something noteworthy.
This feature is very useful for database administrators who perform periodic index maintenances at regular intervals of time. This option provides us with the flexibility to pause, start, and abort the index rebuild operations. Of course, there is overhead on storage, but, in general, this is a pretty cool feature.
Here is an outline of the SQL 2017 Resumable Index Rebuild features and other considerations.
- Better planning and a greater flexibility in the management of indexes during maintenance windows. Provides an option to pause and restart an index rebuild operation multiple times.
- Flexibility to recover from index rebuild failures, since the process does not necessarily have to start from the beginning.
- Space can be a game-changer (storage constraint), when an index operation is paused—both, the original index and the newly created one require disk space.
- Better log space management since it enables truncation of transaction logs during an index rebuild operation.
- SORT_IN_TEMPDB=ON is not supported.
Syntax
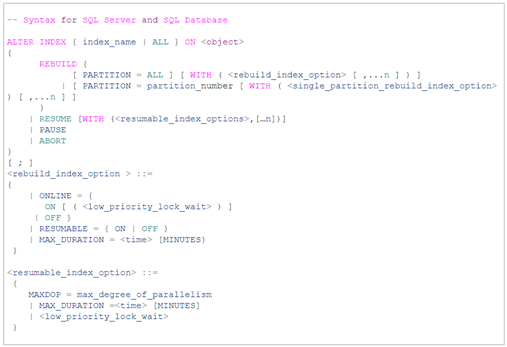
Limitations
- The SORT_IN_TEMPDB=ON option is not supported
- Resumable index operations are not supported on disabled index
- Columnstore index is not supported
Implementing Resumable Indexes with Example
Execute an online index rebuild as a resumable operation with MAXDOP=1.
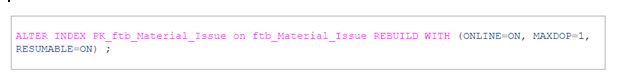
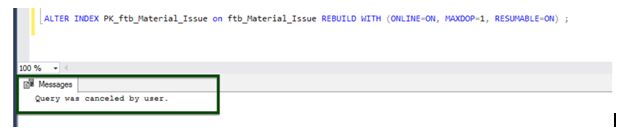
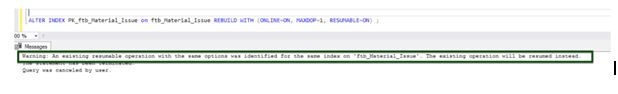
The second run with the same options would reveal that there is already a process with the same options running; we can resume it from where it stopped.
After running it for a few seconds, stop or cancel the execution, and check for the statistics using sys.index_resumable_operations.
The sys.index_resumable_operations is a system view that monitors and checks the current execution status for resumable index rebuild. Let’s now look into the view to understand the state of the operation. This view gives us details of the progress of the entire operation, such as the total number of index pages allocated by the operation. The following query shows our operation that was paused.
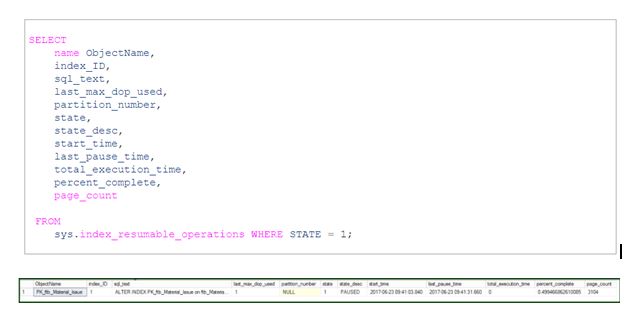
The sys.index_resumable_operations column details
| Column name | Data type | Description |
| object_id |
int |
Every object has an ID, called the object identifier. |
| index_id | int | This is the unique index identifier; this field is not nullable either; index_id is unique only within the object. |
| name | sysname | This is the unique name of the index. |
| sql_text | nvarchar(max) | This is the DDL T-SQL statement text |
| last_max_dop |
smallint |
Self-explanatory, this is the last MAX_DOP used (default = 0) |
| partition_number |
int |
This is the partition number. For non-partitioned objects, or in case all partitions are being rebuilt, the value of this column is NULL. |
| state |
int |
Boolean-like operational state of the resumable index: 0=Running 1=Paused |
| state_desc | nvarchar(60) | Description of the state of the index (Running or Paused) |
| start_time | datetime | Self-explanatory, the start time of the index operation. |
| last_pause_time | datatime | The last pause time of the index operation. If the operation is running and was never paused, the value would be NULL. |
| total_execution_time |
int |
Total run time from start time (in minutes) |
| percent_complete |
real |
The progress of the index operation (in %). |
| page_count |
bigint |
The total number of index pages allocated by the index build operation. |
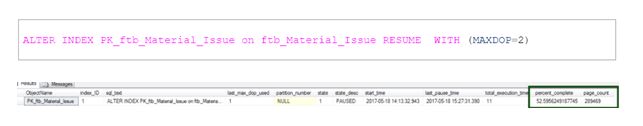
Let’s resume the rebuild operations after 10 minutes and gather the stats.
After cancelling the query execution and status of the index rebuilding operation of clustered index is at 52% complete, and the database size has increased to 2200 MB.
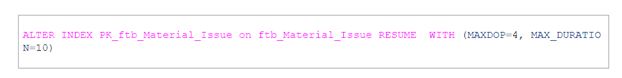
To resume the process with MAXDOP 4 with MAX_DURATION of 10 minutes.
To pause/resume and abort a running resumable online index rebuild
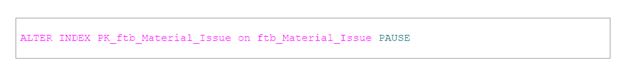
Manage blocking
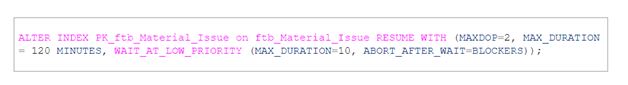
The periodic locking and blocking can be handled effectively by setting WAIT_AT_LOW_PRIORITY. resume the online index rebuild by setting MAXDOP to 2, set the execution time for the index being running as resumable to 120 minutes, and in case of an index being blocked on the lock, wait 10 minutes, and after that, kill all blockers.
Conclusion
Effective t-log management and flexibility to handle indexes at a very granular level eases the huge burden on the database administrator, for the index maintenance operation. Although the online operation is recommended, it’s important that the underlying infrastructure is evaluated, and the implications are understood before proceeding.
The impact of using the resumable option on performance is no different than using the normal command. This is tested with a compressed table and partitioned table. As a recommended practice, you should run the index operations offline, or at least during off-business hours, in order to ensure minimal impact to daily operations.
In this article
